Understanding Thyroid Cancer: Insights from a Thyroid Cancer Doctor

Thyroid cancer is a critical health concern affecting thousands of individuals worldwide. While the diagnosis can be daunting, understanding the disease and the role of a thyroid cancer doctor can empower patients and their families. In this article, we delve deeply into the nuances of thyroid cancer, its treatment options, the importance of early detection, and the vital contribution of healthcare professionals in managing this condition.
What is Thyroid Cancer?
The thyroid, a butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of the neck, produces hormones that regulate the body's metabolism, heart rate, and temperature. When abnormal cells in the thyroid grow uncontrollably, thyroid cancer can develop. There are several types of thyroid cancer, including:
- Papillary thyroid cancer: The most common form, often affecting younger women.
- Follicular thyroid cancer: Typically occurs in older adults and may spread to other parts of the body.
- Medullary thyroid cancer: Can affect both males and females and may be inherited.
- Anaplastic thyroid cancer: A rare but aggressive form, often requiring prompt medical intervention.
Recognizing Symptoms of Thyroid Cancer
Understanding the symptoms of thyroid cancer is critical for early detection. Common signs include:
- A noticeable lump or nodule in the neck
- Changes in voice or hoarseness
- Difficulties swallowing or breathing
- Persistent cough not associated with a cold
- Enlargement of lymph nodes in the neck
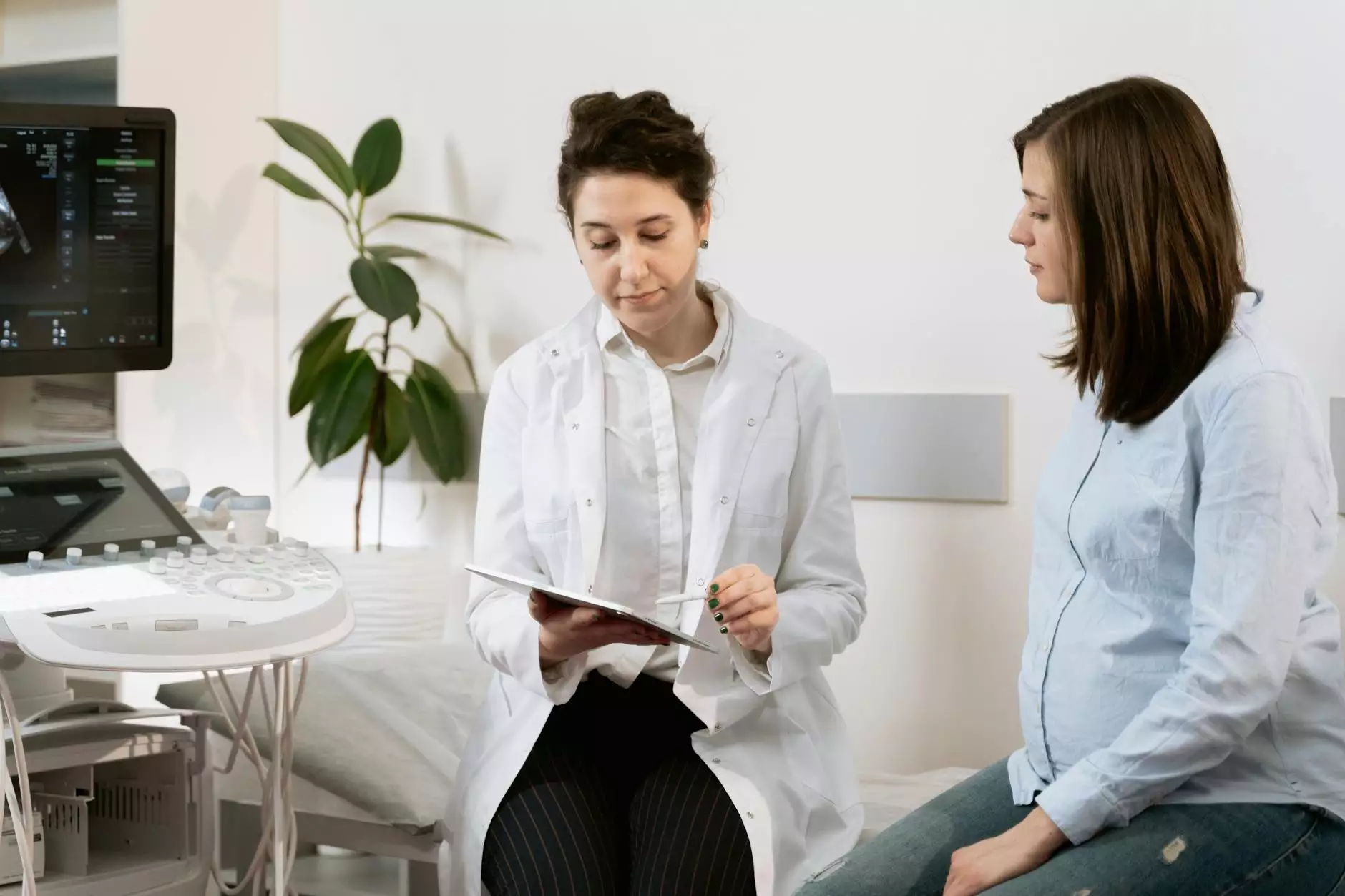
If you experience any of these symptoms, it's essential to consult a thyroid cancer doctor for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of thyroid cancer can significantly enhance treatment outcomes. Regular check-ups and monitoring for symptoms can lead to timely interventions. A thyroid cancer doctor uses various diagnostic tools, including:
- Ultrasound: A non-invasive imaging test to check for nodules or abnormalities.
- Fine-needle aspiration biopsy: A procedure to remove a small sample of thyroid tissue for analysis.
- Blood tests: To measure thyroid hormone levels and check for cancer markers.
- CT and MRI scans: These imaging tests help determine the extent of cancer spread.
Treatment Options for Thyroid Cancer
The treatment for thyroid cancer largely depends on the type and stage of the disease, as well as the patient's overall health. Treatment options include:
1. Surgery
Surgery is often the first line of treatment for thyroid cancer. The primary surgical options include:
- Thyroidectomy: Partial or total removal of the thyroid gland.
- Lymph node dissection: Removal of nearby lymph nodes that may contain cancer.
2. Radioactive Iodine Therapy
Post-surgery, patients may receive radioactive iodine therapy to eliminate any remaining cancer cells. This treatment is particularly effective for certain types of thyroid cancer, especially after a total thyroidectomy.
3. External Beam Radiation Therapy
For cases where the cancer is more advanced or has spread beyond the thyroid, external beam radiation therapy may help shrink tumors and relieve symptoms.
4. Chemotherapy
While not commonly used for thyroid cancer, certain situations may call for chemotherapy to manage aggressive forms of the disease.
5. Targeted Therapy
For advanced thyroid cancers that don't respond to conventional treatments, targeted therapies may be employed. These focus on specific molecular targets associated with cancer.